Fatty acids are chemically a mix of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. They are essential for the normal functioning of our body tissues.
Its deficiency creates many harmful effects on our body. Our body can synthesize most of the fatty acids from the diet we eat but certain fatty acids cannot be synthesized from our body and need to be eaten in the form of food.
Fatty acids are commonly referred to as fats, and not all fats are unhealthy, let these be the facts that let you chose between the truth and the myths.
The Various Types of Fatty Acids are:
In structure and chemical composition, fatty acids vary according to the size and bonds of the carbon chain. So, they can be classified as:
• Short Chain Fatty Acids
Small carbon chains which are non-aromatic combined with hydrogen form small chain fatty acids. They are water-soluble and thus, easily get absorbed by our intestines.
• Medium Chain Fatty Acids
Medium Chain Fatty acids contain a carbon chain of up to 12 carbon atoms, even these can be rapidly absorbed by our intestines and are then transported to the liver bound to the albumin.
• Long Chain Fatty Acids
Long-chain fatty acids have more carbon molecules as the name suggests. They have around 14 to 18 carbon atoms and thus, hardly ever dissolve in water, and finally, these fatty acids end up in the circulatory system.
• Very Long Chain Fatty Acids
The very long chain fatty acids have almost 20 carbon atoms linked together. As the chains are very long thus, they do not dissolve in water at all and hence are not absorbed by our intestines, and just like the long chain fatty acids, these also end up in our circulatory systems.
Also, another common classification is:
• Saturated Fatty Acids
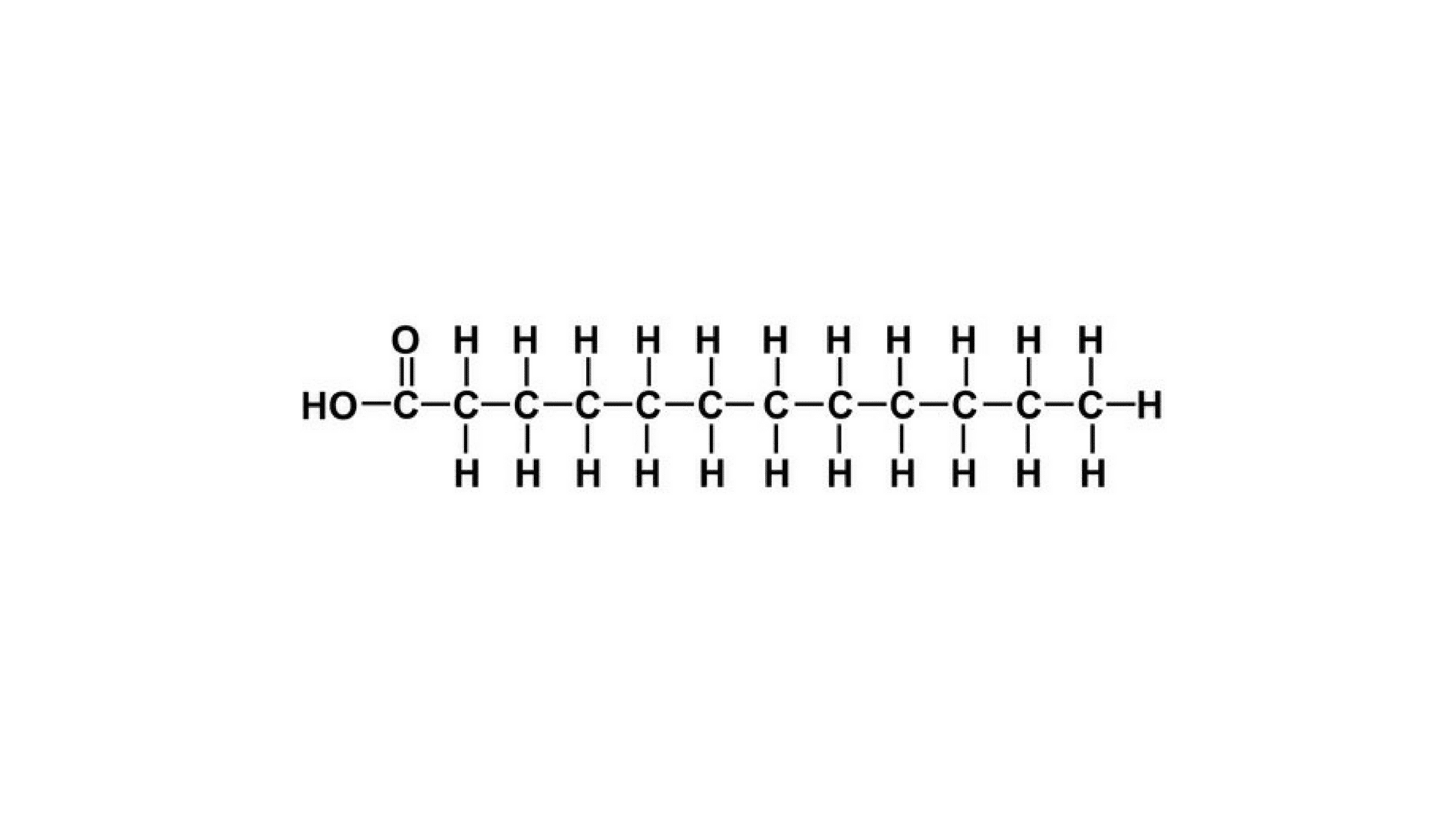
Single bonds between the carbon atoms bind the fatty acid chains of this category. The highly saturated fats are received from animal sources, including butter, milk, and meat.
These are typically solids at room temperature. It is not one of the healthiest options available for consumption.
Though unlike most of the myths that saturated fats are harmful, it should be noted that no clinical studies indicate the same. Rather I would like you all to know better about these facts than to believe word of mouth from various unknown sources which have been publicized so much that they sound like facts.
• Unsaturated Fatty Acids
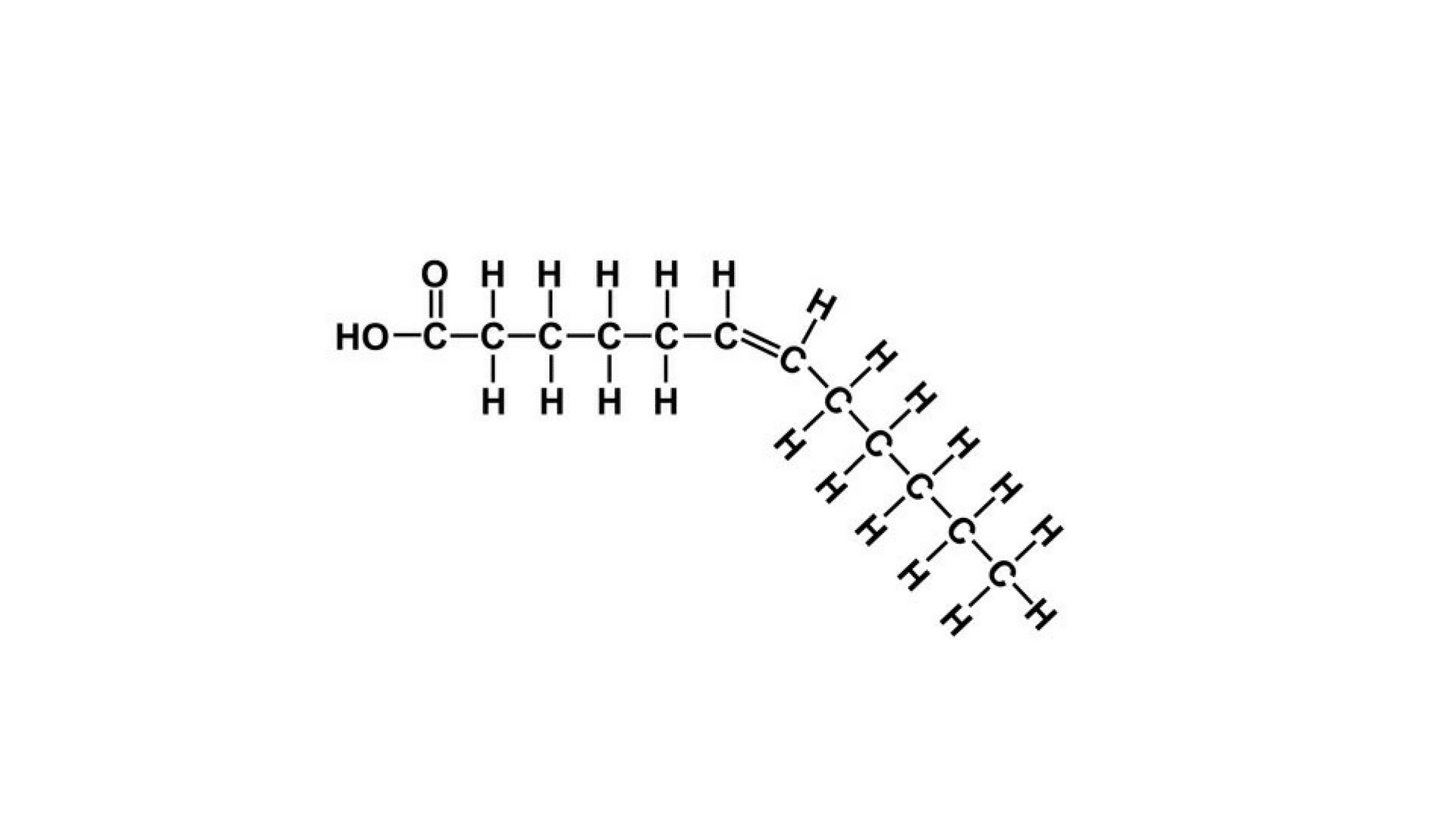
These fatty acids generally have one or more carbon double bonds thus reducing the hydrogen from the chain. Its major sources are plants, and these are generally liquid at room temperature.
Unsaturated fatty acids can be of two types:
(a) Monounsaturated Fatty Acids
When there is just one double bond of carbon, and thus only one hydrogen is missing then we call the fatty acid to be monounsaturated. Monounsaturated fat increases the good cholesterol and helps in lowering bad cholesterol in our body, thus, helping us prevent cardiovascular issues.
(b) Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
When more than one double bond of carbon is present in the chain, then the fatty acids are called polyunsaturated. It is believed that polyunsaturated fats also reduce the risk of many common illnesses for our health.
• Trans Fatty Acids
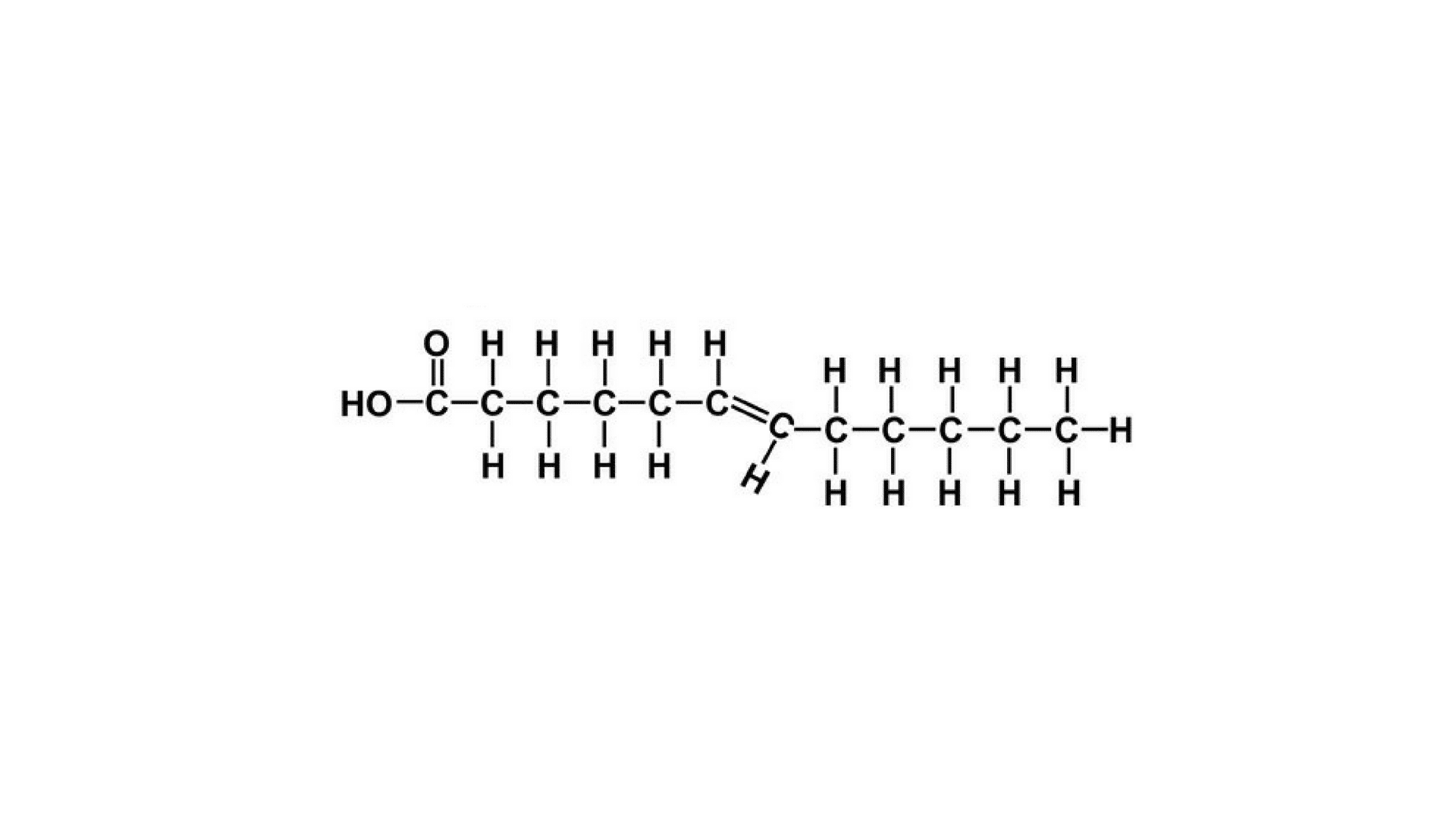
This is the fatty acid that we should avoid as trans fatty acids have a certain twist, i.e., even though there are double bonds yet the hydrogen levels are not much altered thus, creating a rift and making them stick to the cell lining. As they get attached to the lining, there is a risk of free radical attack which can destroy the entire cell altogether. It is our responsibility to warn you all against the side effects of trans fats as these may lead to the following conditions:
Trans fats increase inflammation in people especially the ones suffering from obesity.
Apart from these there are other types of fatty acids as well like:
• Essential Fatty Acids
These fatty acids refer to that group which our body is unable to prepare even after breaking other nutrients. Like the Omega 3 and Omega 6 are two essential fatty acids which we can only acquire by having a diet rich in both of them and our body can produce omega 9 and so omega 9 is not an essential fatty acid.
• Oxygenated Fatty Acids
The major fatty acid present in castor oil is called ricinoleic acid, it is an example of the Oxygenated Fatty Acids. These contain keto, hydroxyl and epoxy groups.
• Cyclic Fatty Acids
These fatty acids contain a cyclic unit with three or five like prostaglandins and sometimes even six carbon atoms.
Fatty acids as the famous myth goes are bad for health but let me inform you that if required quantities of fatty acids are not consumed then our body can show severe symptoms like:
- Brittle Nails
- Dry Skin
- Scaly Skin
- Patchy Skin
- Dandruff
- Cracked Fingertips and Heels
Apart from these noticeable features that make us realize that our body has been deficient. We might as well feel lethargic and tired. Now not only adverse effects but fatty acids also have benefits too, like:
- It protects our brain, i.e., it helps in preventing neurological disorders.
- Fatty acids promote heart health.
- Fatty acids help in controlling anxiety and depression.
- Consumption of fatty acids helps in combatting inflammation.
These are just a few benefits, it has a number of benefits to offer.
The major sources of fatty acids are:
Flaxseed oil, Soybean oil, Sunflower oil, Safflower oil, Hempseed oil, Pumpkinseed oil, Perilla oil, Chia seeds and walnut oil.
Conclusion
The benefits of fatty acids truly make me believe that instead of believing in things that are just said and heard we should always research about the various benefits of a product, understand its source and then decide if the product being offered is worth its consumption or not?
The last will be a request in the words of Dr. Catheleen London rightly influenced us in her words when she stated that “Flax Seed is a good fat. The Omega-3 fatty acids, every cell in your body needs them.” So going by the word essential fatty acids not only need their fulfillment in the form of diet but we also need to make sure that our body lacks none of them.